The best gift that any girl and woman dreams of is a diamond ring. This is an expensive pleasure, so you should choose with special care. Let's look at what criteria are used to choose a diamond ring.
The best gift that any girl and woman dreams of is a diamond ring. This is an expensive pleasure, so you should choose with special care. Let's look at what criteria are used to choose a diamond ring.
Choosing a diamond using the “4 C” system
Does everyone know that a diamond is a cut diamond, inconspicuous in appearance? Not every diamond has all the cutting properties. It is a mistake to believe that the main thing in a gemstone is its size.

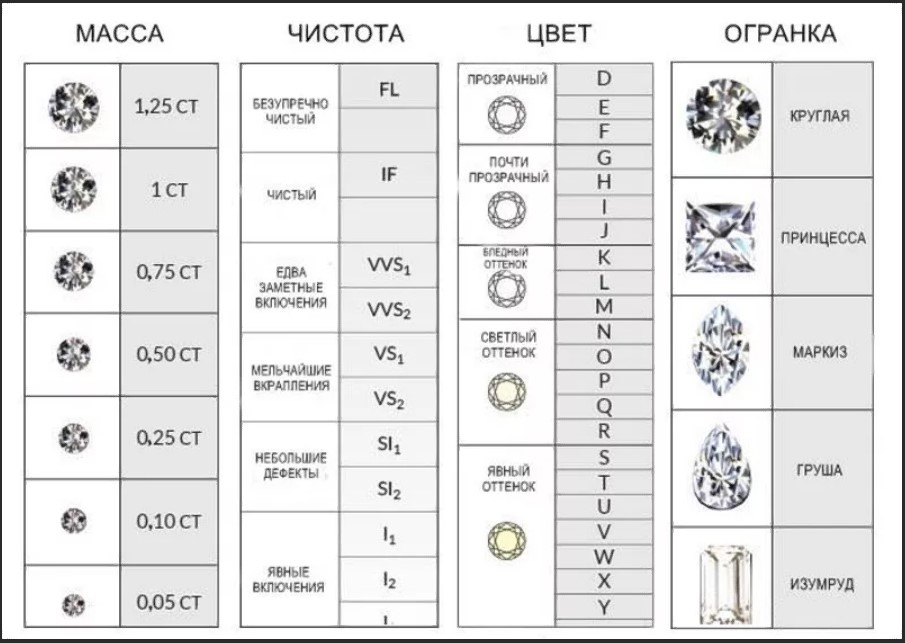
The quality of all diamonds is determined according to an international system called the “4 Cs”:
- cut – cut;
- clarity – purity;
- color – color;
- carat – weight.
Cut
The luxurious shine and play of light are the merit of a diamond cutting specialist. Most often, diamonds are given a round shape. But natural forms can be varied: “drop”, “triangle”, “baguette”, etc.
Diamond shapes

Princess
This stone is in the shape of a square (rectangle), has sharp corners, and small edges.
Marquis

Boat shape with different proportions.There are long and round stones.
Heart

The most popular shape, it is chosen for wedding or engagement rings. The stone has 57-58 facets, and the sizes can vary, as can the proportions.

Emerald
The diamond is in the shape of a rectangle, the corners are beveled, and the edges are made in steps.
Rose

This round stone is very similar to a flower, the top has 24 equal sides, and the base is smooth and flat.
Radion (Usher)

Very similar to the “Princess” shape, but here the corners are beveled for better fixation in any frame. They look impressive for stones with shades.

A drop
The drop shape is rarely found in rings, more often in earrings or pendants.

When choosing an engagement ringand, it is better to give preference to the types: “Princess”, “Heart” or “Marquis”.
The master, looking at the shape of the diamond and its flaws, selects the most suitable cut option.

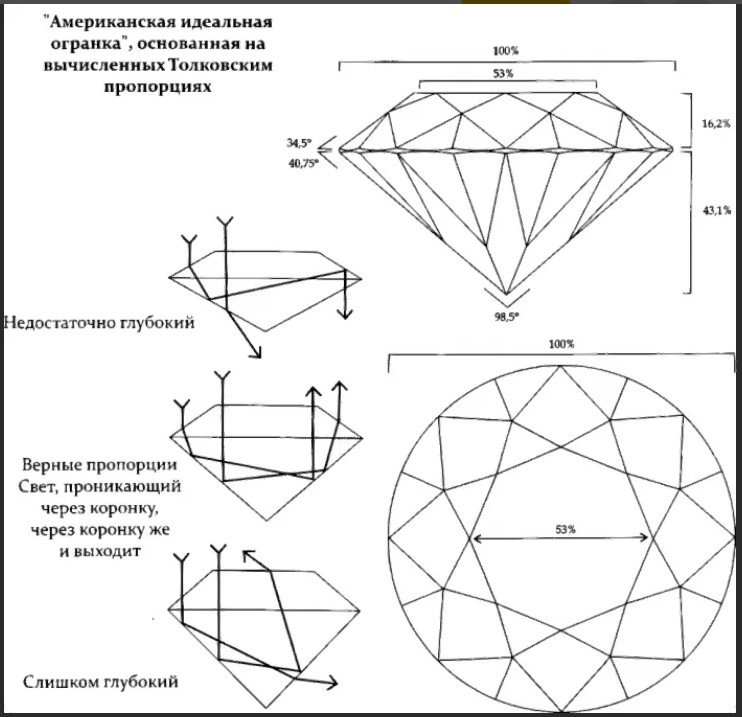
From the right one cut proportions diamond will be affected by the refraction of light inside the stone. This is what gives the stone its famous shine. The main thing is proportions, i.e. the ratio of the size of the diamond to the shape of its facets.
Different cut classes
The gradation is subjective, based on visual perception products. For the classic (round shape) there are 7 points in the D-Z color range:
- brightness (number of reflected rays);
- fire (shades of reflected rays);
- flickering (when moving the diamond);
- weight;
- durability;
- polishing quality stone;
- symmetry of cut.
Items are evaluated separately, everything is important for a specific stone.

Abroad, there is another gradation of 5 points:
Excellent - means dazzling brilliance, i.e. the stone reflects almost all the light that comes inside. It also has liveliness and fire - an even distribution of light and dark areas in the stone.

Very Good – very good quality of the stone, most of the rays are also reflected, shine and fire are at their best. The only difference is that the diamond may have darker highlights at the edges or in the center.

Good – These stones lack shine and shimmer; they can sometimes be darker in girdles. Here attention is paid to the relationship between weight and pattern, so the stone will have a lower cost than previous ones.

Fair – Although the light rays are reflected, they immediately come out of the stone; there is a darker area that passes around the girdle and the platform. For items up to 85 carats, this is acceptable, since it is difficult to distinguish externally.

Pool – the stone is considered bad, i.e. disproportionate, with little flicker. The color is dull even to a layman's eye.

In Russia, a letter cut classification is used:
A – ideal;
B – good;
IN - satisfactory;
G - bad.
Here also the diameter is taken as 100%, and the rest are expressed as a percentage of it.
For A and B everything is ideal, but up to 4 are possible small knifes (i.e. parts of the surface without polishing). Minor defects can only be in the depths of the stone.
Purity
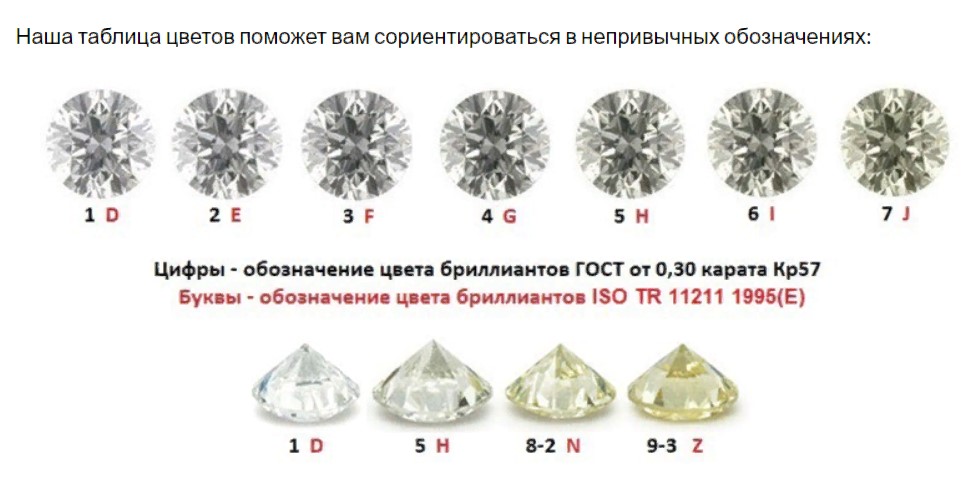
There are 11 groups in terms of cleanliness in international GIA system And in Russia 12 points:
- 1 – perfect transparency;
- 2-4 – scanty inclusions;
- 5-6 – small inclusions, but clearly visible when magnified;
- 7-8 – already noticeable inclusions;
- 9-12 – inclusions will be noticeable even without magnification.
You should choose a ring encrusted with diamonds, and not artificially ennobled ones. Small diamonds (no more than 0.29 carats) are the most expensive, with a color of 1-4.
Important! Pure diamonds of higher quality are set in platinum or white gold to avoid reflections of the yellowness of the metal.
Color

The shades of stones depend on the presence of impurities; they absorb some of the light, and therefore give a certain shade. Most diamonds have a yellowish tint: from colorless to brownish.
But Rare colors are found in natural conditions:
- pink – if they stay at high temperatures;
- blue ones have boron impurities;
- green - with uranium, etc.
Red ones are very rare, as well as burgundy and unusual gray ones, but their price is incredibly high.

Weight
The smallest stones weighing 0.001 carat diameter approximately 1 mm. One carat is equal to 0.2 g. If the proportions or cut are not ideal, the stone will lose its brilliance and spectacular shine.

Reference! For round stones use the formula:
Carat = Length x width x height of stone x 0.0061
Carat content is calculated in millimeters.
Differences between natural diamonds and cubic zirconias and fakes
A natural diamond always has impurities and voids, so a diamond will always be visible in clear water, and a fake, even a perfect one, will be transparent (invisible).

50 carat diamond ring
It is easy to distinguish a real diamond from a laboratory one (this is cubic zirconia) as follows:
- Breathe on the diamond, the condensation will stick to the cubic zirconia longer than on a diamond.
- The color spectrum is richer on artificial stone.
- Natural minerals often have various defects.
- The simulator will be somewhat heavier than natural stone.

Our recommendations will help you understand the difficult task of choosing a diamond ring for an engagement, wedding, or as a gift to a loved one.


 0
0