With the help of modern technologies, it is possible to imitate leather in such a way that it is very difficult to distinguish it from natural one. Such a product will look like the original and even smell like it.
How to distinguish leather from imitation
 The store has a very large selection of leather goods. At the same time, sellers are not always truthful with the buyer and may offer artificial material under the guise of natural material.
The store has a very large selection of leather goods. At the same time, sellers are not always truthful with the buyer and may offer artificial material under the guise of natural material.
First thing You need to pay attention to the price of the product. Real leather doesn't come cheap.
It will also be useful to have an idea of the types of leather, since the area of application depends on its properties.
Kinds
- Boiled. The leather is highly durable and quite lightweight. It got its name from the method of dressing. In ancient times it was used as armor or in book bindings.
- Vegan. The starting material is cattle or pig leather with a thickness of one cm. It is used in ethnic costumes, accessories, holsters and saddles.
- Velours. Absolutely any skins are suitable for its production.The finished version looks like this: on the right side is the bakhtarma (that is, the fleecy part), on the left is the mereya (leather part).
- Suede leather. The starting material is the skins of wild animals. The material is soft, velvety and wear-resistant. It is covered on both sides with short dense pile.
- Laika. Made from the skins of lamb or kid. The feel of a product made from such leather is soft and plastic. Mereya is smooth and without wrinkles. Gloves and rarely jackets are made from this material.
- Nappa. When finished, it is a very thin material (up to 1 mm) and elastic. Made from the skins of cows, bulls or sheep. Nappa is used to make bags, accessories, hats and clothing. Main producers: Italy, Spain and Türkiye
 Napplak. This is a type of nappa, only varnished.
Napplak. This is a type of nappa, only varnished.- Nubuck. Externally very similar to suede. Its difference is that it is made from the skins of cattle.
- Deer. Quite durable material that holds its shape and retains heat well. Feels like suede. Very rarely found on sale, so they are expensive.
- Parchment. Produced from the skins of lamb, goat and calf. It is used in the manufacture of musical instruments, car trim, book bindings and accessories.
- Morocco. Made from the skins of calf or sheep. The quality of this material is thin, soft, wear-resistant and comes in different colors. Bags and cases are made from it.
- Split. Made from pig skins. As a result, a material of different thicknesses is obtained, which is used in the production of various products (from haberdashery to outerwear).
- Cheprak. It is made from skins taken from the backbone of cattle. It has significant density and thickness.
- Shagreen. It is made from the skins of the spinal part of small cattle or horses. Often colored green. Has a bumpy surface. Depending on the method of dressing, soft and hard shagreen is distinguished.
- Chevrette. This material is dense and elastic. Made from sheep skin.
- Kid. The basis for production is goat skins. It differs from chevrette in its “fine wrinkle” pattern. The material is soft, dense and durable.
- Shora. The production is based on cow or bull skins. It differs from saddle cloth in that it is denser and thicker.
- Yuft. It is made from the abdominal part of the skin of a cow or bull. It is distinguished by softness and plasticity.
 There are a lot of varieties of material. It is difficult for an inexperienced person to understand it. Therefore, it is better to learn to distinguish it from artificial one.
There are a lot of varieties of material. It is difficult for an inexperienced person to understand it. Therefore, it is better to learn to distinguish it from artificial one.
There are not so many types of leather imitation. Its application depends on the base. Since different materials provide different elasticity and strength.
Types of artificial leather
- Dermantin. The basis of this material is cotton. Nitrocellulose coating (on one or both sides).
- Kirza - This is cotton with a rubber coating.
- Vinyl leather - This is a synthetic fabric coated with polyvinyl chloride. Maximum imitates natural leather.
- Stretch leather. The base is knitwear. Polymer coating.
- Eco leather (PU). Widely used in modern products. It is based on defective genuine leather. The coating is made of high quality polymer coating.
- PVC. The basis is fabric. PVC coating with added plasticizer.
Heat exchange
 The material is designed to protect the body from cold and heat. Therefore, its entire structure is aimed at these functions. Even the most modern artificial material has much worse heat transfer.
The material is designed to protect the body from cold and heat. Therefore, its entire structure is aimed at these functions. Even the most modern artificial material has much worse heat transfer.
Therefore, when choosing clothes or shoes for a cold winter, it is better to give preference to natural materials. You won't feel hot or cold in this product. Also, genuine leather is elastic and takes the shape of its owner. Such shoes will not press, causing discomfort.
Wrinkling
Leatherette only looks like genuine leather. It does not have all the qualities and benefits of natural. It is less elastic and therefore quickly cracks and bursts. Genuine leather does not have such defects. It simply takes the form of the person who wears it.
In-store verification methods
 Modern technologies have made great strides forward. Artificial leather is so similar to natural leather that it is difficult to distinguish it by eye.
Modern technologies have made great strides forward. Artificial leather is so similar to natural leather that it is difficult to distinguish it by eye.
IMPORTANT! Do not test the product with fire. Products made from natural materials can be coated with a special compound that is highly flammable. But artificial leather does not withstand temperatures and can melt. In this case, you will have to pay for the damage.
- Take the product in your hands. Hold it for a minute or two. Genuine leather heats up quickly and absorbs moisture from your hands. This product will be warm and dry. And the artificial one will become wet.
- Examine the sections of the product. For natural material it will be rough, while for artificial material it will be smooth.
- Genuine leather is elastic and quickly recovers after pressure.
- The natural material is porous and, when dyed, completely absorbs the dye. Therefore, if you slightly stretch natural leather, its color will not change and cracks will not be visible.
- The porosity of natural leather is arbitrary, but that of artificial leather is the same.
- Look at the cuts. Leatherette is based on fabric. In genuine leather, the natural weave of the fibers will be visible.
- Expensive products always have a sample of the material. You can examine it for fibers, try to wet it (natural leather will quickly absorb moisture).
- Bend the product. In artificial leather, the creases will remain visible, but in natural leather they will quickly return to their original position.
- The suede is checked by lightly stroking it. If the deviated pile has changed color slightly, then it is a natural material.
Documentary proof of quality
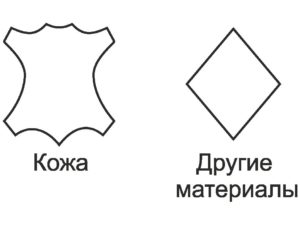 Leather products are marked with distinctive signs. From them you can determine which parts are made of genuine leather and which are made of leatherette.
Leather products are marked with distinctive signs. From them you can determine which parts are made of genuine leather and which are made of leatherette.
If there is a diamond sign on the label, then this is an artificial material. For natural skin, a designation is used that resembles the appearance of animal skin (figured image).
European manufacturers often write designations of natural leather on their products: England - genuine leather, Italy - vera pelle, France - cuir, Germany - echtleder.
Checking at home
 If you have a question: “How to check a product for imitation leather?” You can test the product at home, based on the main properties and differences between imitation and natural ones.
If you have a question: “How to check a product for imitation leather?” You can test the product at home, based on the main properties and differences between imitation and natural ones.
There are several ways
- Faux leather is less porous and therefore repels water, while natural leather absorbs. Provided that the product is not waxed or varnished.
- Place your palm on the product. If you quickly feel heat transfer. This is a natural product.
- You can check it with a lighter. But some manufacturers of imitation leather add substances to its composition that prevent it from melting. Natural material smolders, and imitation melts.



 0
0






Maybe it's still DERMATIN? How is this possible, you went to school after all?